Vaccine
The medical companies Quadrant Holdings (UK) and Chiron Vaccines (USA) have developed a new vaccination substance based on Trehalose that is resistant to temperature.
Standard vaccinations are not resistant to ambient temperatures, they need to be cooled in order to be implemented for vaccination campaigns. This cooling requires a special effort in rural areas of developing countries and relief engagements during disasters. The logistic networks of refrigeration and transport are called “cold chains” and are handled by various approaches, e.g., storage in caves that are packed with ice on the Afghan-Pakistan border, or in a more sophisticated setup, by solar powered, ice-producing refrigerators developed by the WHO.
The goal of eliminating the cold chain itself to save energy, efforts and costs is met by the medical development of Trehalose based vaccines.
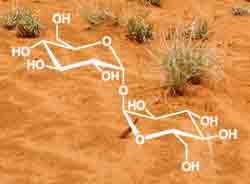
Trehalose is a disaccharide sugar found in plants, fungus, moss and in insects, it has been discovered to have a stabilizing effect at ambient temperatures to protect desert species from damage during periods of drought.
This effect can be applied for stabilizing vaccines and pharmaceuticals against ambient temperatures. At the moment Quadrant and Chiron are working on a combination vaccine against diphteria, tetanus and whooping-cough (pertussis) for children with a Trehalose formulation.